What is a Class?
The Class in PHP is basically the same
as in other languages such as Java. The class definition begins with the
keyword class, followed by a class name. The form name can be any name
except a reserved word or keyword in PHP. The class name is followed by a pair of curly braces which contain the definition of class members and methods.
| Example of a Class |
| <?php |
| Class abc |
| { |
| //member functions and variables go here |
| } |
| ?> |
What is an Object?
An Object is an enclosed bundle of
variables and functions which is copied from a Class. Objects provide an
easy interface and hide a lot of their inner workings. The object sends
orders through special functions called methods and they can return
information.
While creating a Class, a set of
characteristics is laid down. By creating Objects of that type, entities
are created that share these characteristics but the Object might
initialize them as different values.
| Example |
| Suppose there is a class named building. This class would have a characteristic named floor. All the objects of class building would share the characteristics of floor, but some would initialize it to “one”, some to “two”, others to “three” or “four”, and so on. |
The benefit of object oriented code is
that it is re-useable. In this the classes can be used to create
different objects and classes from one project can be used in other
projects as well. Child classes can also be created which inherits the
properties of the parent classes.
Creating an Instance
To start with, a class having no member functions and
variables is not useful. For a class to be completely useful, member
functions and variables have to be added in that class. Let’s take an example of a class with a variable in it.
| Example |
| <?php |
| Class abc |
| { |
| $a = “Hello!”; |
| } |
| ?> |
The class abc is the basis from which many objects can be instantiated. The new
keyword is used to create an object. Now any abc object that is created
contains a property called $a with the value of “Hello”. This property
can be accessed and even be changed with the help of objects.
In this the -> operator is used to access or change the properties of the object.
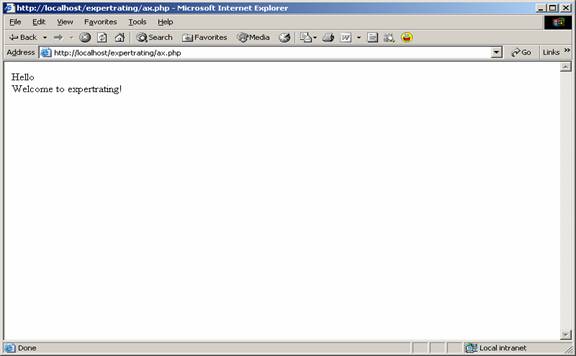
In the following example $obj1 and
$obj2 are the objects of the class abc. In this $obj2 has been assigned
the string “Welcome to expertrating!” to its $a property.
| Example |
| <html> |
| <body> |
| <?php |
| Class abc |
| { |
| var $a = "Hello"; |
| } |
| $obj1 = new abc(); |
| $obj2 = new abc(); |
| $obj2->a = "Welcome to expertrating!"; |
| echo "$obj1->a<br />"; |
| echo "$obj2->a<br />"; |
| ?> |
| </body> |
| </html> |
Extends
Another feature of object oriented
programming is used in PHP, which is inheritance. In PHP a class a class
can inherit methods, functions and members of other class by using the extends
keyword in the declaration. In PHP it is not possible to inherit from
multiple classes, a class can inherit from only one base class.
The class from which inheritance is
done is called the parent class or base class and the class which
inherits is called the child class.
The Keyword Final
The final keyword prevents the child classes from overriding a method. This can be done by prefixing the method with the keyword final. If the complete class is being defined as final then that class cannot be extended.
| Example |
| final class test |
| { |
| //methods and functions |
| } |
Abstract
A new concept of abstract classes
and methods has been introduced in PHP5. When a class is defined as
abstract then it is not allowed to create the instance of that class. A
class that contains at least one abstract method must also be abstract.
The methods defined as abstract cannot define the implementation; they
just declare the method’s signature.
When a child class is inheriting from
an abstract parent class, then all the methods marked abstract in parent
class declaration must also be additionally defined by the child class.
These methods must be defined with the same or weaker access. This
means that if an abstract method is declared as protected in the parent
class then it must be declared either as protected or public in the
child class.
Static Keyword
When
class members or methods are declared as static then there is no need to
instantiate that class. These members and methods are accessible
without the instantiation of the class. If a member is declared as
static then it cannot be accessed by an instantiated class object, but a
method declared as static can be accessed by an instantiated class
object.
The static declaration of a class must be after the
visibility declaration (means that after the member or method has been
declared as public, protected, or private). The static method calls are resolved at compile time and static properties cannot be accessed through the object through the arrow operator (->).
Interfaces
Object interfaces allow the creation of a code which
specifies that which method a class must implement, without having to
define how these methods have to be handled. Interfaces are defined in the same way as a class is defined. These interfaces are defined with the keyword “interface”. In the interface the contents of the methods do not have to be defined and all the methods declared in the interface must be declared as public.
Implementation of Interfaces
To implement an interface, the implements
operator is used. The methods must be defined before implementation and
all the methods in the interface must be implemented within a class.
Exceptions
Exception handling in PHP is similar to
that of other programming languages. Within a PHP block of code we can
throw, try and catch an exception. There must be at least one catch
block in a try block. In this multiple catch blocks can be used to catch
different class types. In exception handling the execution will
continue after the last catch block has been encountered and exceptions
can be thrown within catch blocks.
In exception handling when an exception
is thrown, the code following the statement will not be executed rather
PHP will attempt to find the first matching catch block. If the
exception is not caught then it will result in a fatal error with an
uncaught exception message.
No comments:
Post a Comment